
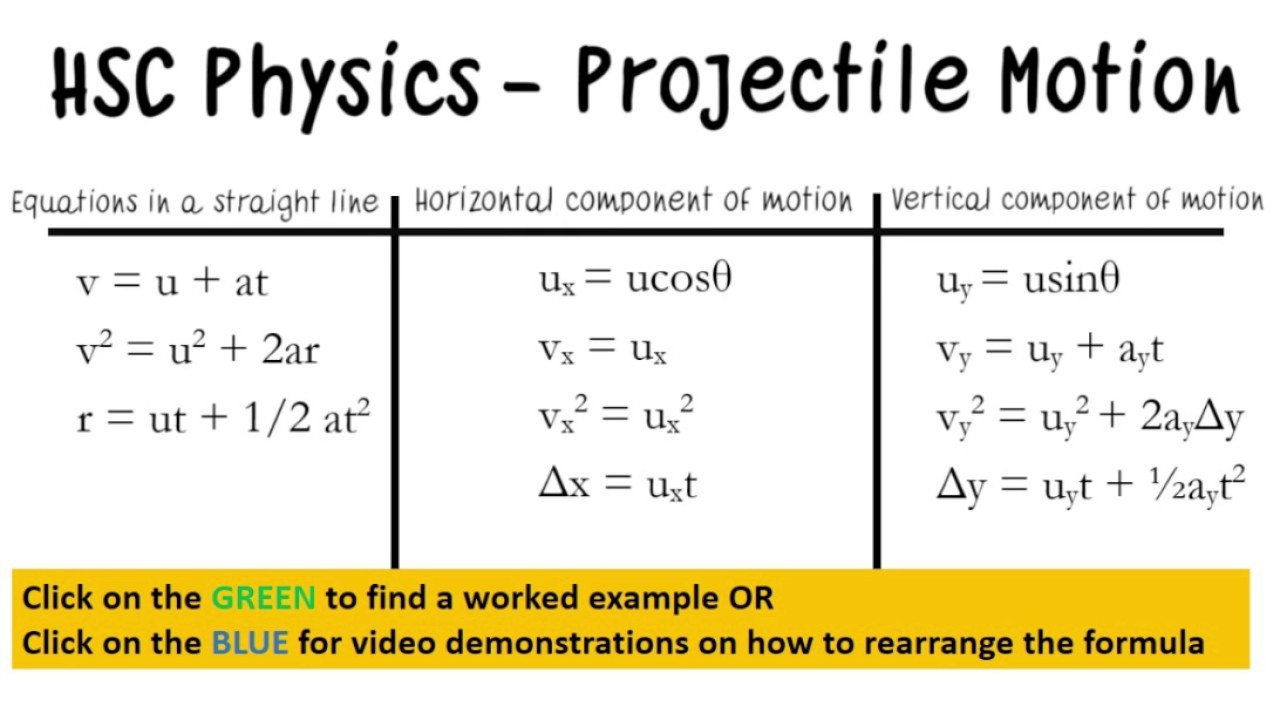
It is not required that we use this choice of axes it is simply convenient in the case of gravitational acceleration. (This choice of axes is the most sensible because acceleration resulting from gravity is vertical thus, there is no acceleration along the horizontal axis when air resistance is negligible.) As is customary, we call the horizontal axis the x-axis and the vertical axis the y-axis. The key to analyzing two-dimensional projectile motion is to break it into two motions: one along the horizontal axis and the other along the vertical. We discussed this fact in Displacement and Velocity Vectors, where we saw that vertical and horizontal motions are independent.
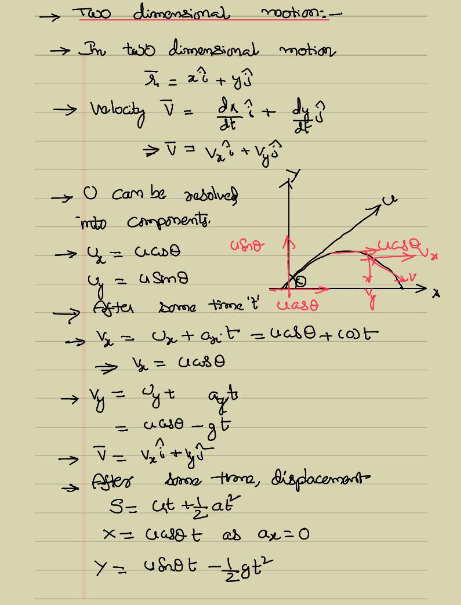
The most important fact to remember here is that motions along perpendicular axes are independent and thus can be analyzed separately. In this section, we consider two-dimensional projectile motion, and our treatment neglects the effects of air resistance.

The motion of falling objects as discussed in Motion Along a Straight Line is a simple one-dimensional type of projectile motion in which there is no horizontal movement. The calculation for throwing the objects away can easily be. In the above equation, h is the height of the object from where the object is thrown, t is the time, and g is the gravitational acceleration. Such objects are called projectiles and their path is called a trajectory. To determine the distance of the vertical components of the velocity for projectile motion can be written as. Some examples include meteors as they enter Earth’s atmosphere, fireworks, and the motion of any ball in sports. The applications of projectile motion in physics and engineering are numerous. Projectile motion is the motion of an object thrown or projected into the air, subject only to acceleration as a result of gravity. Calculate the trajectory of a projectile. Once you know that, you can use the vector equation vu+at (which is just the definition of acceleration when acceleration is uniform), and the related dut+0.5.Find the time of flight and impact velocity of a projectile that lands at a different height from that of launch.Calculate the range, time of flight, and maximum height of a projectile that is launched and impacts a flat, horizontal surface.Use one-dimensional motion in perpendicular directions to analyze projectile motion.By the end of this section, you will be able to:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
